
Logical – The logical network topology is a higher-level idea of how the network is set up, including which nodes connect to each other and in which ways, as well as how data is transmitted through the network.Setup, maintenance, and provisioning tasks require insight into the physical network. Physical – The physical network topology refers to the actual connections (wires, cables, etc.) of how the network is arranged.The question of, “What is network topology?” can be answered with an explanation of the two categories in the network topology. The way a network is arranged can make or break network functionality, connectivity, and protection from downtime. These diagrams are essential for a few reasons, but especially for how they can provide visual representations of both physical and logical layouts, allowing administrators to see the connections between devices when troubleshooting. The design and structure of a network are usually shown and manipulated in a software-created network topology diagram. A streamlined and properly managed network topology can increase energy and data efficiency, which can in turn help to reduce operational and maintenance costs. Choosing the right topology for your company’s operational model can increase performance while making it easier to locate faults, troubleshoot errors, and more effectively allocate resources across the network to ensure optimal network health.

Above all, it plays an essential role in how and how well your network functions. The layout of your network is important for several reasons. Logical network topology is a little more abstract and strategic, referring to the conceptual understanding of how and why the network is arranged the way it is, and how data moves through it. Physical network topology, as the name suggests, refers to the physical connections and interconnections between nodes and the network-the wires, cables, and so forth. There are two approaches to network topology: physical and logical.

Each has advantages and disadvantages and depending on the needs of your company, certain arrangements can give you a greater degree of connectivity and security. Just as there are many ways to arrange and maintain a city-such as making sure the avenues and boulevards can facilitate passage between the parts of town getting the most traffic-there are several ways to arrange a network.

Think of your network as a city, and the topology as the road map. Network topology refers to how various nodes, devices, and connections on your network are physically or logically arranged in relation to each other. What Tools Help Manage and Monitor Networks? What Is Network Topology?
#How to scale network topology mapper software#
I’ll also discuss the use and benefits of network topology mapping software like SolarWinds ® Network Topology Mapper in configuring your network, visualizing the way devices connect, and troubleshooting network issues. The key is to understand your objectives and requirements to create and manage the network topology in the right way for your business.įollowing an in-depth network topology definition, this article will look at the main types of network topologies, their benefits and drawbacks, and considerations for determining which one is best for your business. Several tasks go into effective network topology management, including configuration management, visual mapping, and general performance monitoring.
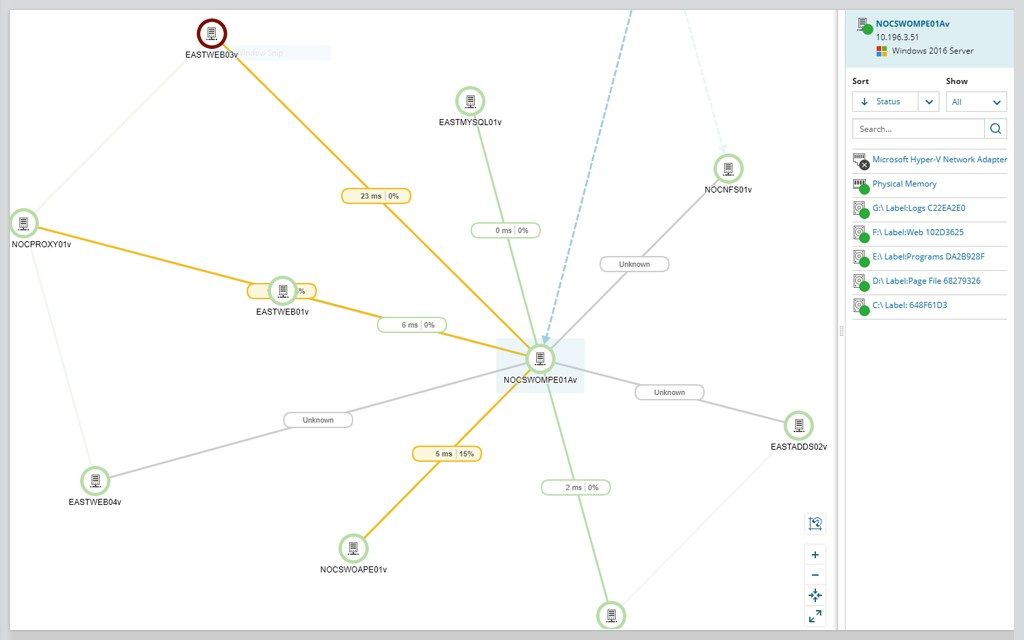
Admins have a range of options when it comes to choosing a network topology, and this decision must account for the size and scale of their business, its goals, and budget. There are numerous ways a network can be arranged, all with different pros and cons, and some are more useful in certain circumstances than others. Network topology is the way a network is arranged, including the physical or logical description of how links and nodes are set up to relate to each other. The configuration, or topology, of a network is key to determining its performance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
